Published
Node.js Performance: Array.concat() vs the spread operator
What is the best way to concatenate arrays in JavaScript?

In JavaScript there are two ways to combine arrays. Using the old standard Array.concat()
method. Or the more modern spread operator (...). But which method is the most
performant way to combine arrays?
This article will help you find the purr-fect way to con-cat-enate your arrays!
Table of contents
- The Different Ways to Combine Arrays
- Testing Methodology
- The Test Machine
- Results
- Conclusions
- So, what is the best way to combine arrays in JavaScript?
- Feedback
The Different Ways to Combine Arrays
Array.concat()
const combined = array1.concat(array2);This is the traditional way to combine two arrays, simply call the concat()
function of the one array with the second array as the input. Then you get a new
array with the combined data of both arrays without modifying the original arrays.
The Spread Operator (...)
const combined = [...array1, ...array2];This is a more modern way to combine two arrays. As with concat() the original
arrays are not changed by using the spread operator.
Array.flat()
const combined = [array1, array2].flat();This method is a bit out there, but I found myself reaching for it when trying to make code more readable. Ultimately I didn’t stick with it as the results will show.
Testing Methodology
As with my previous benchmarking of loops, I used the Tinybench library. The benchmarks simply combine an array with itself to make a new array. This test was run against different array lengths to see if one method or another was more effective at different sizes.
The tests also use different run times to compare performance across engines. Currently, the engines included are:
- Node.js v18
- Node.js v20
- Node.js v22
- Bun v1.1.18
- Deno v1.44.4
You can see the full test suite over at my GitHub Repo.
Browsers weren’t considered for this test as I’m mainly focusing on server-side JavaScript engines.
The Test Machine
The machine I’m running these tests on is a System76 Darter Pro 8. It has a 12th-generation Intel CPU that clocks in around 4.70 GHz (model i7-1260P). And it has 32 GB of RAM.
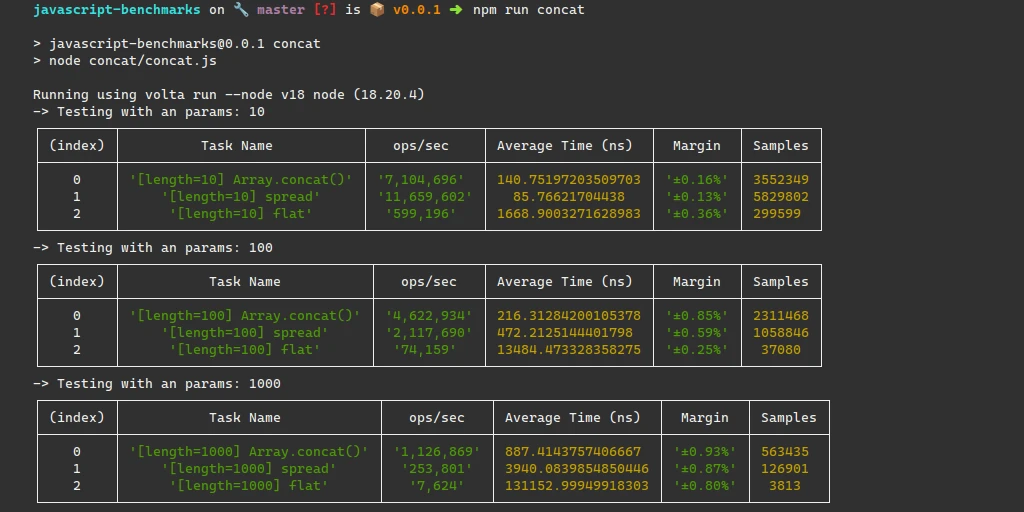
Results
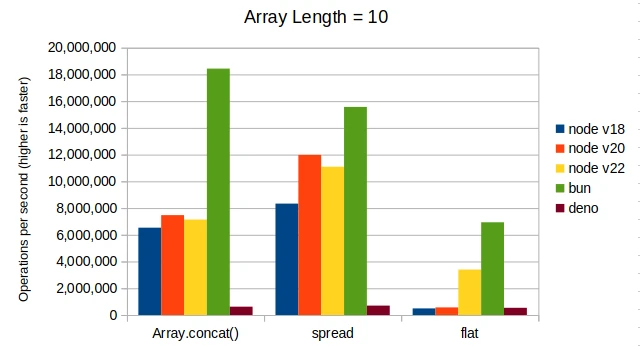
Here are the results combining two arrays with lengths of ten, one hundred, one thousand, and one hundred thousand.
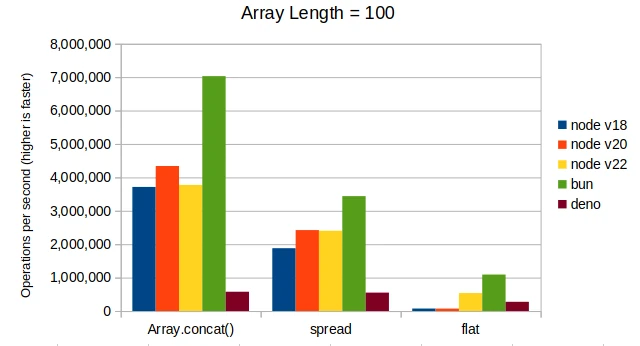
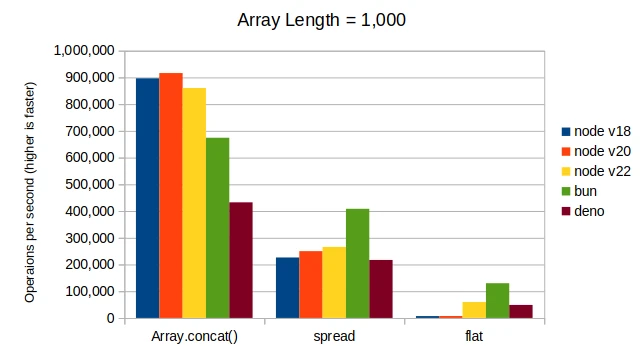
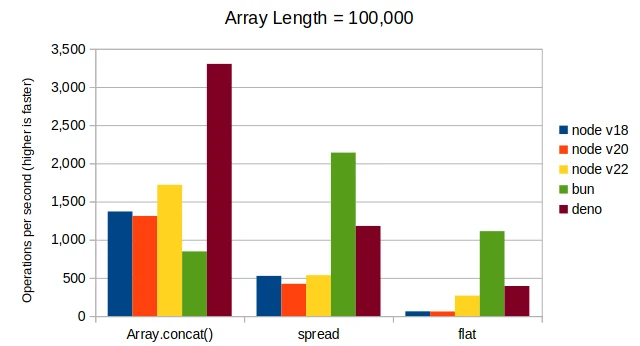
Conclusions
For Node.js, Array.concat() is more performant when combining arrays of length
around 100 and more. For Bun, Array.concat() is more performant at any array length.
The Array.flat() fails to perform well at any array length. Plus, it is a little
weird so it doesn’t provide a very good developer experience.
So, when you know the array sizes will remain small, using the spread operator
can be good for developer experience. However, most of the time Array.concat()
will be more performant.
The spread operator can be used in other contexts, like when using iterators.
To quote this Stack Overflow answer:
“Performance-wise concat is faster, probably because it can benefit from array-specific optimizations, while ... has to conform to the common iteration protocol.”
So, what is the best way to combine arrays in JavaScript?
Array.concat() is the most performant way to combine arrays in JavaScript at
most array lengths. It is well understood and optimized compared to the spread operator.
Feedback
If you have any feedback on my testing methodologies or suggestions for improvement, just create an issue on my GitLab repo for this blog or on the GitLab repo for the benchmarks.